Introduction to CI/CD & CI/CD Pipeline
A Beginner's guide to CI/CD and CI/CD pipeline, with its advantages in the industry.
With the ever-evolving tech industry, it's crucial to deliver bug-free code expeditiously, this is where a CI/CD pipeline plays a pivotal role. But what is CI/CD, let's learn about it in this blog.
Overview
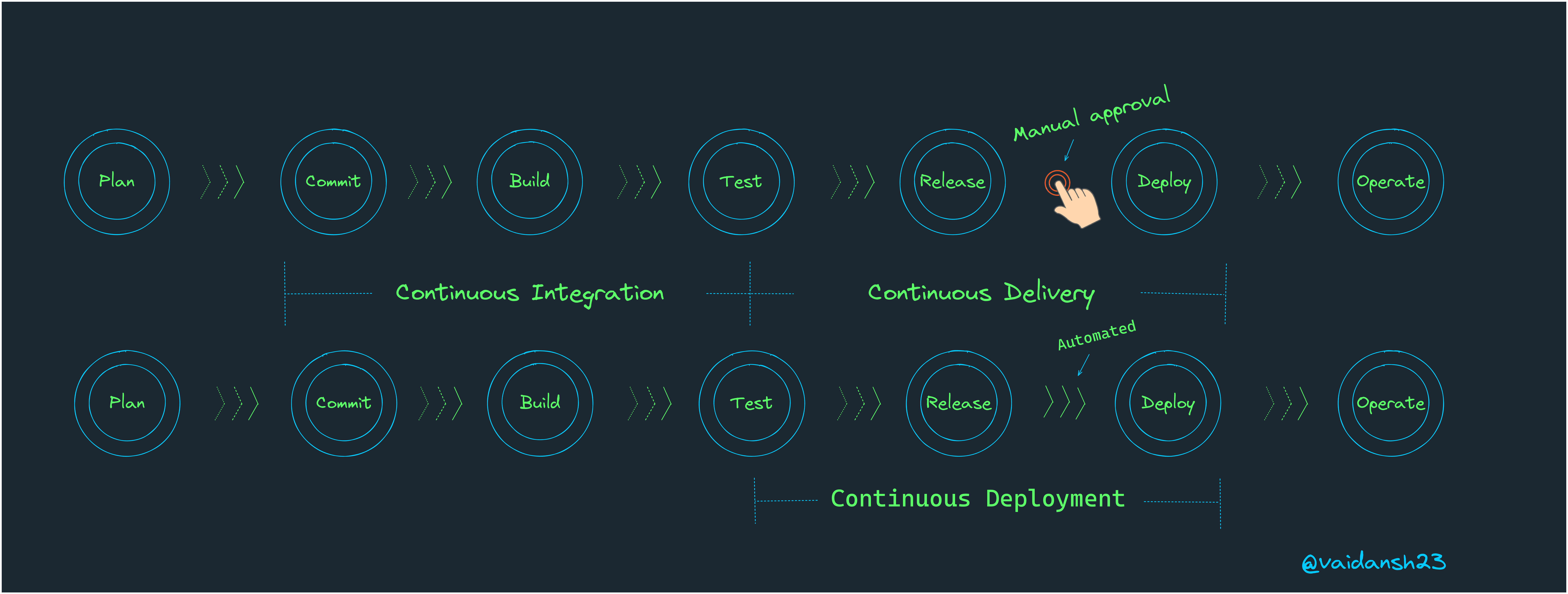
Firstly, CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration/ Continuous Delivery, there's another segment to CI/CD called Continuous Deployment which is an extension to Continuous Delivery. Now let's take a look at these terms individually.
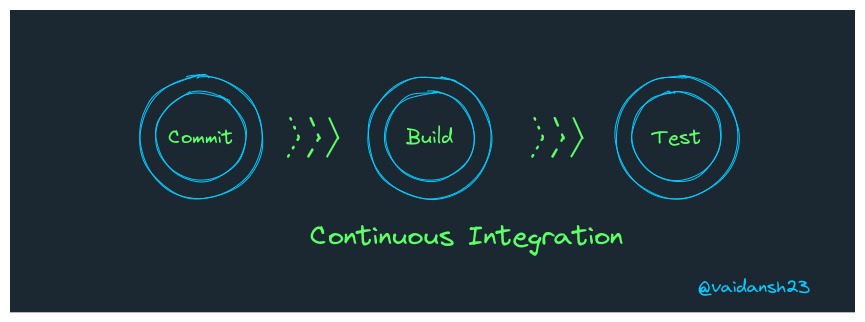
Continuous Integration
Definitions
- A practice of merging all developers' working copies or changes to the main branch
Here's another definition
- The practice of automating the integration of code changes from multiple developers into a single project.
Now, let's understand these definitions in detail:
- Consider several developers working on a project.
- Now, these developers will individually make changes in the codebase in their own repositories.
- These changes are supposed to be merged into the repository of the main project after they are validated by going through automated tests.
- The previously mentioned tests ensure that the changes made are following the particular guidelines, standards that are established for the given project.
- Now the changes which pass these tests are automatically merged into the main repository of the project.
- The above changes can take place in various time periods (multiple times a day,
everyday, every hour, etc...) depending on the organization.
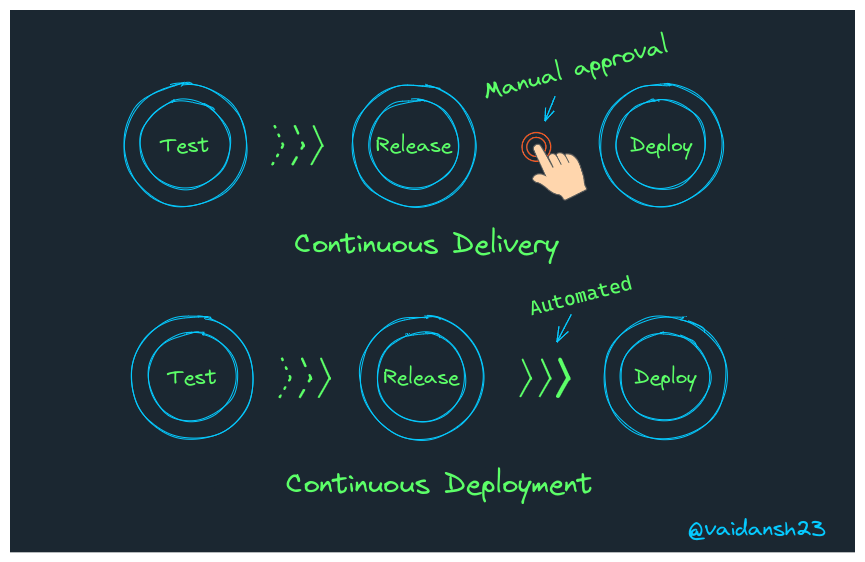
Continuous Delivery
Definitions
- An approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that each build is potentially good to be released at any time.
Here's another one
- Continuous delivery is a software development practice that uses automation to speed the release of new code.
Let's have a deeper look:
- We have already seen that Continuous integration is the automated testing of the code changes made by the developer, now we have an automated release process where we can deploy our application at any time by just clicking a button.
- Theoretically speaking, we can deploy/release daily, weekly or at any time(which suits the organization) with the help of Continuous Delivery.
- CD involves testing, staging and deployment of code/application.

Continuous Deployment
- Now, in CD the deployment in a production environment can either be approved by a human or can be done automatically without any explicit approval.
- The latter one is called Continuous Deployment.
- Definition- A strategy in which all the changes are automatically deployed for production after CI.
So now we know that Continuous Deployment is basically the automation of Continuous Delivery.
- Visuals help make things clear, so here's one:
CI/CD Pipeline
Definitions
- CI/CD pipeline automates the software delivery process, from building code to running tests and further deploying a new version of the software.
Here's the second one
A CI/CD pipeline is a series of orchestrated stages that can take the source code from development to effectively producing/deploying the application.
Have a closer look at this diagram(click on it to get a broader view) for a better understanding:
Stages in a CI/CD Pipeline:
There are various steps in a CI/CD pipeline like Building, Packaging, Testing, Validating, Verifying the infrastructure, and Deployment. Let's have a look at the 4 main stages:
I. Source stage
Firstly, the CI/CD pipeline has to be triggered to initiate the process. The pipeline can get triggered by making any change in the code or the program and can even be done manually. Initializing a pipeline manually is not recommended as it defies the whole concept of automating things and can even cause issues if not triggered on time.
Some of the tools commonly used in this stage are:
- GIT
- AWS CodeCommit
- SVN (Apache Subversion)
II. Build Stage
In this stage, the source code is combined with all its corresponding dependencies to create an executable instance of the application/product which can be potentially shipped to the end-user or client.
This stage plays a vital role, any sort of failure in this stage usually indicates a fundamental error in the codebase underneath.
If development is taking place in a compiled language like Java, C/C++ or Go, then the compilation of the program has to take place. Contrarily, programs written in languages like Python, Ruby, and JavaScript bypass this step. Nevertheless, cloud-native software are usually deployed in Docker irrespective of the language.
Some tools commonly used in this stage are:
- Jenkins
- AWS Code Build
- Gradle
- Maven
III. Testing Stage
Now we've entered the testing stage of our application. Here, we'll be running automated tests to validate the efficiency of our code and the functioning of our software.
The purpose of this test is to deliver bug-free software to the end-user, to ensure this, the code goes through multiple automated tests which are designed by the developer depending on the size and complexity of the software.
Any sort of failure in this stage brings light to the problems in the code which were not anticipated by the developer when writing the code.
Some tools commonly used in this stage are:
- Appium
- Jest
- Selenium
- JUnit
IV. Deploy Stage
Now we're at the final stage of the pipeline, considering the software has passed all the prior tests now it's ready for deployment. The software is usually deployed in various environments like beta, staging, etc... These stages help in Quality Assurance as the product is used internally by the developers and the beta testers. After this, the software goes into a production environment for the end-users.
This stage includes containerization technologies and tools like:
- Docker
- Kubernetes
- Terraform
- Ansible
- AWS Code Deploy
- Azure Pipelines - Deployment
Advantages of CI/CD
There are a lot of advantages to practising CI/CD, let's have a look at some of'em:
1. Smaller Code Changes
CI/CD helps in integrating small code changes at one time. These changes are simpler to handle and have fewer unintended consequences.
These small changes help the developers in recognizing an issue much sooner before a significant amount of progress is made, because these changes can be tested as soon as they are integrated into the main code repository.
2. Reduce Risk
Bugs are time-consuming and demanding to fix once they are found late in the development stage. This problem escalates once the software is already released for production.
This is where CI/CD pipeline becomes a rescuer, as we can test and deploy code more frequently, giving developers the facility to detect bugs and fix them in real-time.
3. Fault isolation
Fault Isolation refers to the practice of designing systems which reduce the scope of negative outcomes when any error is found. In this way, we can reduce the potential for damage done to our software/system.
This kind of approach helps in lowering the consequences of any undetected or unresolved complication.
4. Reduced Mean Time To Resolution(MTTR)
Mean Time To Repair/Resolution represents the average time required to troubleshoot or repair a product or system failure.
With the help of CI/CD, the MTTR is reduced because of the smaller code changes and quicker fault isolation.
5. Accelerated Release Cycles
As the failures spontaneously detected, they will be repaired quickly, leading to accelerated release cycles. Here, a seamless CI/CD pipeline will help in making multiple releases, as the code will be kept in a release-ready state after thorough testing.
6. Reduced Backlog
CI/CD helps in reducing the small, non-critical problems which in turn clears the backlog for developers, providing them with a lot more time to focus on bigger problems which are faced by the organization.
7. Cost Deduction
Now that the number of errors is reduced, this frees up a lot of time for the developers, allowing the organization to focus on the product development as there wouldn't be a need to make immediate code changes. Practising CI/CD pipeline also accelerates the Return Of Investment(ROI).
8. Customer Satisfaction
Meeting the end-user's requirements is the top priority of a team. CI/CD helps in making daily changes which are requested by the end-users based on their feedback, resulting in better usability improvement and higher customer satisfaction.
9. Easier Maintenance and Frequent updates
Regular and precise updates with effective maintenance is crucial in creating a great product. Practicing it during non-critical hours when the traffic is low provides a better edge over other products.
10. Enhanced Team Transparency and Accountability
CI/CD helps receive continuous feedback from the team members, which in turn encourages responsibility and the accountability of the whole team.
Conclusion
CI/CD is an important part of DevOps which is extensively used in a lot of famous organizations such as Amazon, Netflix, Target, Walmart, Facebook, etc… The topic of CI/CD doesn't end here, there's a lot more to explore in the domain of CI/CD and also Devops. Do checkout KubeSimplify for more such blogs.
Thanks for Stopping By ✌️