What is Pod?
It is the smallest deployable and schedulable unit that Kubernetes can manage. It is a best practice that we keep one container inside a given pod, but we can place more than one container inside a pod. Each Pod has its own local IP address inside the cluster
Layout of Kubernetes Pods
Pod is a collection of container(s)
Deployment is a collection of Pod(s)
Pod lifecycle
When we
kubectl apply -f <fileName>
then kubectl converts the YAML manifest to JSON file and sends it to api server
api server authenticate using kubeconfig auth and checks whether the user is authorized or not to a particular functionality (i.e. creation, deletion) (i.e. RBAC)
when it is authorized, all that the data gets persisted to the etcd 😇 here state becomes Pending
Now the Scheduler comes and it finds the best match of the node where it will be running (i.e. iterate through all the nodes in the cluster to get the best possible Node based on the resources or images pulled).
After getting it sends the labels filled with spec to the api server now that particular request is also stored on the etcd 😇 here state becomes Container Creating
api server instructs the kubelet of that particular node about the pod spec which has to be created.
kubelet is responsible to fetch the image from image registry. The cri gets the ip attached to the pod which is in turn send to the api server and again data is stored in etcd 😇 here state becomes Running
Whenever the container dies too many times then 😇 here state becomes Crash loop back off and whenever the container succeded then 😇 here state becomes succeeded
Link to the Source Code comments
Hooks
actions that you want to do before the container starts
Pre-stops hooks When the container has begun terminating then this command is executed
Post-start hook When the container starts then only this is executed
Init container it runs before running the workload container(s)
Init containers
They are container(s) that run to completion and run before the main container starts
use case
- To change the file structure of the mounted volume
- Added configuration to the mounted volume
- It can be used to delay the start-up of the main container so that certain checks are done beforehand However, if the Pod has a restartPolicy of Never, and an init container fails during the startup of that Pod, Kubernetes treats the overall Pod as failed.
When all the init containers are ✅👍🏼 then only the workload container will start there is 🚫 Liveliness, Readiness probe
Multiple container pod
use cases
- For logging purposes of the main application container
- It can be used to act as a reverse proxy to get the static files
Health Checks
Liveliness probe It checks whether the pod is alive or dead /health
Readiness probe It checks whether the pod can get or post requests. /ready
Startup probe It checks whether the application within the container is started. All other probes are disabled if a startup probe is provided until it succeeds.
if it fails then 😇 here state becomes Crash loop back off
http
- name: probes
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: 80
tcp
- name: probes
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 80
exec
- name: probes
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- cat
- /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
- initialDelaySeconds - before any probes start time to delay its start check
- periodSeconds - the time between one probe check to another
- timeoutSeconds - kubelet will wait for this much time for response
- successThreshold - how many times we want the probe to be successful to mark it as SUCCESSFUL
- failureThreahold - how many failures will make kublet restart the container
Limits
Memory If the current usage of memory is more than the allowed then OOME (Out Of Memory Exception) and then 😇 here state becomes Crash loop back off
CPU If the current usage of CPU is more than the allowed then 😇 here state becomes Crash loop back off
Pod Topology Spread Constraints
Volumes
Empty Dir
- ❌ Saving critical data
- gets created as soon as the pod is assigned to the node
- stay throughout the life-span of the pod
- when pod deleted it also deleted
volumes:
- name: test-vol
emptyDir: {}
Hostpath
- ❌ Saving critical data
- it mounts a file or a directory from the node's file system into the pod
volumes:
- name: test-hostpath
hostPath:
path: /dd
type: DirectoryOrCreate
Let's add all that we learned
# Basic resource limits and requests
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: cpu-mem-demo2
spec:
containers:
- name: cpu-mem-demo2
image: ubuntu:latest
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"
memory: "200Mi"
requests:
cpu: "2"
memory: "100Mi"
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--cpu", "2"]
---
# example of the basic multi-container pod, with init container having probe checks
# and volume mounts (i.e. HostPath) to preserve the data after the containers are gone
# Hooks are also there
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-website
labels:
web: dipankar-web
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-server
image: nginx:alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 80
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: 80
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- cat
- '/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html'
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/usr/share/nginx/html/"
name: storage-web
- name: check-network
image: busybox
volumeMounts:
- name: resource-usage
mountPath: "/usage"
command:
- "/bin/sh"
- -c
args:
- while true; do
date >> /usage/data.log ;
egrep 'Mem|Cache|Swap' /proc/meminfo >> /usage/data.log ;
sleep 5;
done
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo Starting!!🚀 >> /usage/log"]
preStop:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo 'Terminating!!🚧' >> /usage/log"]
initContainers:
- name: fetch-website
image: alpine
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/home"
name: storage-web
command:
- "wget"
- "-O"
- "/home/index.html"
- "https://dipankardas011.github.io/dipankardas011/"
volumes:
- name: storage-web
hostPath:
path: /website
type: DirectoryOrCreate
- name: resource-usage
hostPath:
path: /usage
type: DirectoryOrCreate
...
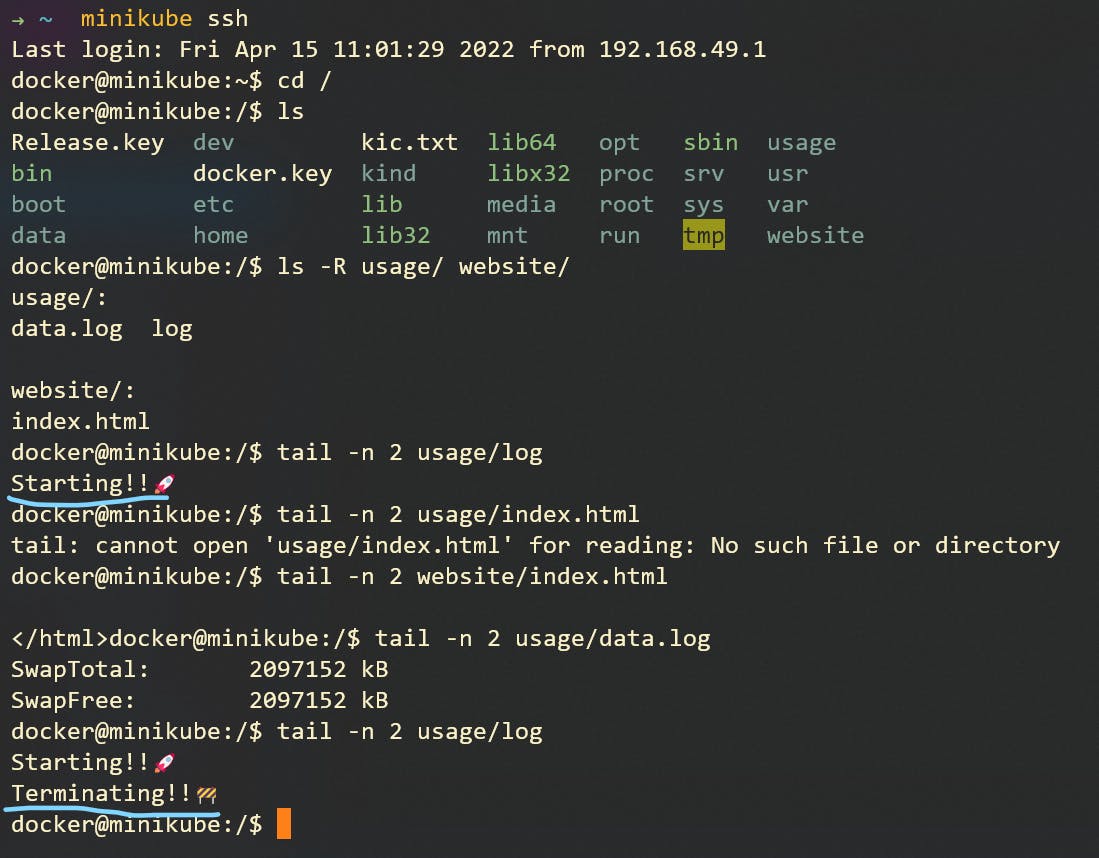
To check the data collected
minikube ssh
cd /
# here you will the folders usage/ and website/